Overview
- Published on August 19, 2025 in Nature Communications, the work comes from a Yale team including lead author Mark Gerstein.
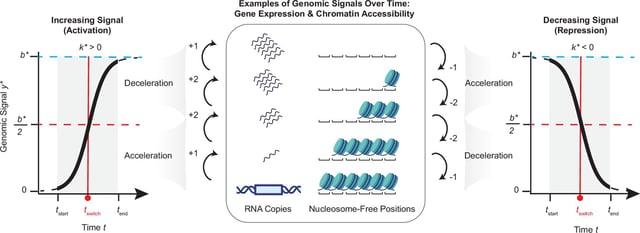
- The method combines a logistic ordinary differential equation with machine learning to quantify when and how rapidly genes turn on or off.
- Applied to developing mouse brains, the analysis grouped genes into accelerators, switchers, and decelerators, with most following simple, gradual trajectories.
- A neural network predicted gene-expression dynamics from nearby chromatin changes, performing especially well for genes under complex regulation.
- The authors say the approach could help pinpoint future therapeutic windows, including a potential “point of no return,” with further validation needed before clinical use.