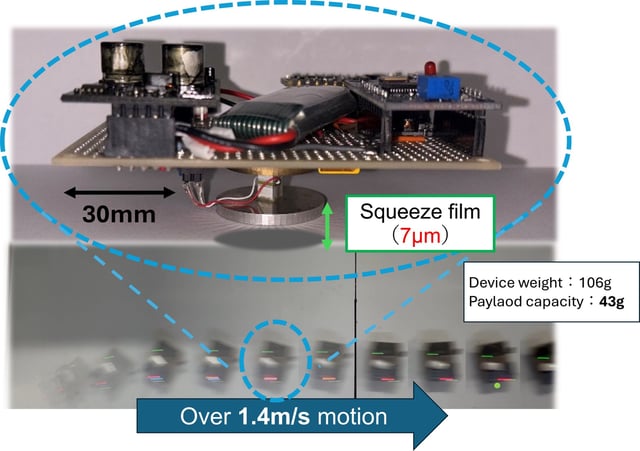
Overview
- The centimeter-scale prototype combines acoustic levitation, a wireless power and control circuit and a piezoelectric actuator to create a squeeze film for untethered, contactless movement.
- Laboratory results confirmed sustained frictionless motion at up to 3 m/s on a 10° incline and showed that deactivating levitation stops the device under gravity.
- Payload tests revealed a total mass limit of 150 g—allowing roughly 43 g of additional load—beyond which levitation and propulsion cease.
- Researchers chose acoustic methods over diamagnetic or pneumatic systems to avoid bulky magnets or pressurized gas, and solved cable interference by integrating a wireless drive circuit.
- Building on peer-reviewed findings, the team is now focusing on energy efficiency, load and terrain stability and the integration of multiple units into robotic contactless-delivery systems.