Overview
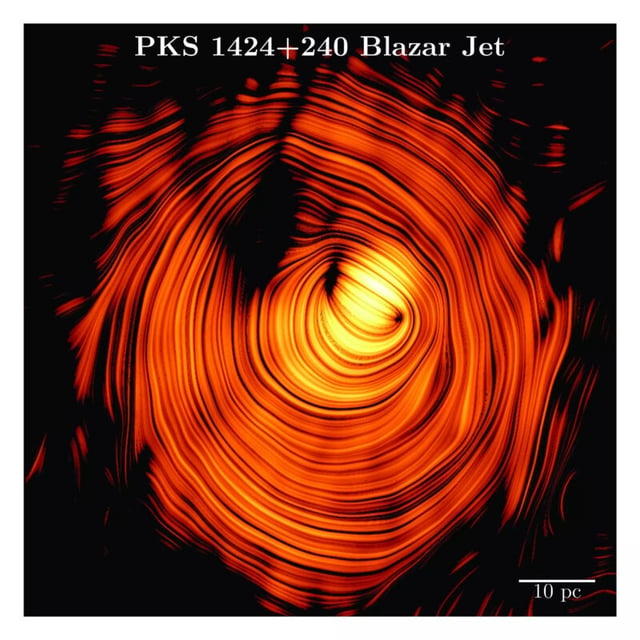
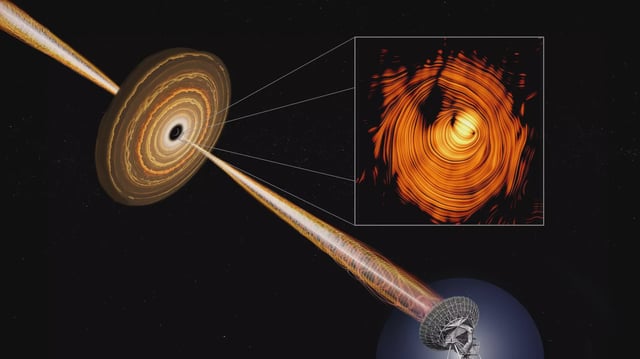
- Astronomers combined 15 years of VLBA/MOJAVE polarization data to create a deep, high-resolution radio image of PKS 1424+240’s jet base.
- The map reveals a near-perfect ring-shaped magnetic field threading the jet, pointing to a helical structure capable of accelerating particles to extreme energies.
- The jet is oriented almost directly toward Earth, producing a brightness boost of roughly 30 while projection effects make its apparent motion look slow.
- The findings link the jet’s magnetic topology to very-high-energy gamma rays and IceCube-associated neutrinos, reinforcing a multi-messenger picture of blazar jets.
- The peer-reviewed study, led by Yuri Kovalev at the Max Planck Institute and supported by the MuSES project, was published in Astronomy & Astrophysics.