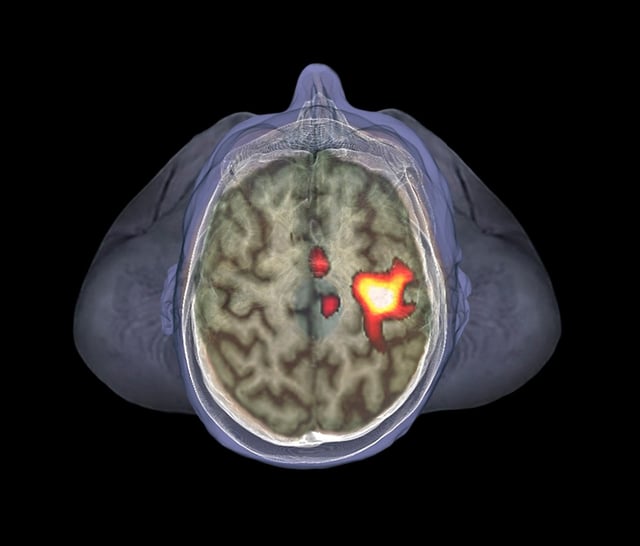
Overview
- Participants exposed to virtual reality avatars displaying infection symptoms mounted early innate immune responses, including activation of innate lymphoid cells and natural killer cells, without real pathogen exposure.
- Functional imaging and EEG showed that sick avatars specifically engaged fronto-parieto-occipital networks and the salience network, triggering faster behavioral reactions to peripersonal threats.
- The immune activation profile elicited by virtual infection cues closely matched the response observed following influenza vaccination in a comparative cohort.
- Study authors caution that use of a single vaccine type and an exclusively young adult cohort limit the generalizability of their findings.
- Researchers are investigating applications of VR-induced immune priming as a potential adjunct for vaccine enhancement, allergy desensitization and non-pharmacological immunomodulation.