Overview
- Peer-reviewed results published on August 20 in Nature detail an international collaboration led by the University of Vienna.
- The technique probes electrostatic potentials by recording tiny deflections of an electron beam passing through a crystal with a Paul Scherrer Institute camera.
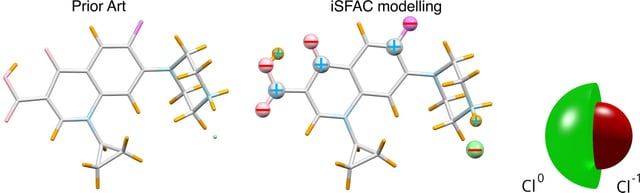
- An analysis approach called ionic scattering factor modeling models each atom as both neutral and charged to quantify partial atomic charges.
- Demonstrations on ZSM-5, tyrosine, histidine, tartaric acid, and the antibiotic ciprofloxacin show broad applicability across catalysts, amino acids, and pharmaceuticals.
- In ciprofloxacin hydrochloride, the chloride ion carries about 40% of a full negative charge, highlighting strong environment-dependent charge distributions relevant to drug and materials design.