Overview
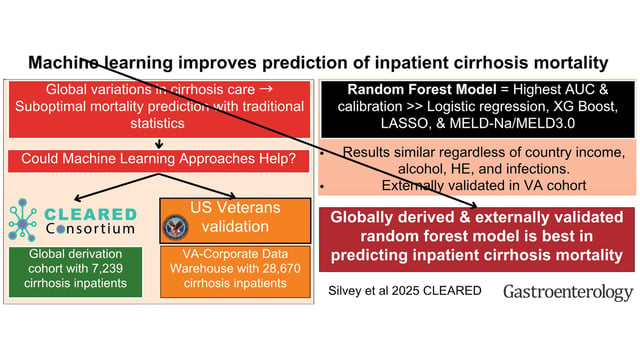
- Random Forest algorithm trained on 7,239 patients from 115 centers in 36 countries achieved an AUC of 0.815, surpassing traditional logistic regression and LASSO models
- External validation in 28,670 U.S. veterans confirmed consistent predictive accuracy across high-, upper-middle- and low-income settings
- A streamlined version using the top 15 variables maintained strong performance with an AUC above 0.85, enhancing global scalability
- Key admission-day predictors include acute kidney injury, hepatic encephalopathy, infection status, MELD-Na score, albumin level and white blood cell count
- Early risk stratification at admission supports intensified monitoring, transplant evaluation or hospital transfer to improve patient outcomes