Overview
- An SSA.gov account provides personalized benefit estimates based on your actual earnings history and inflation adjustments.
- Social Security calculates benefits using your top 35 years of earnings, treating any gap years as zero in the average indexed monthly earnings formula.
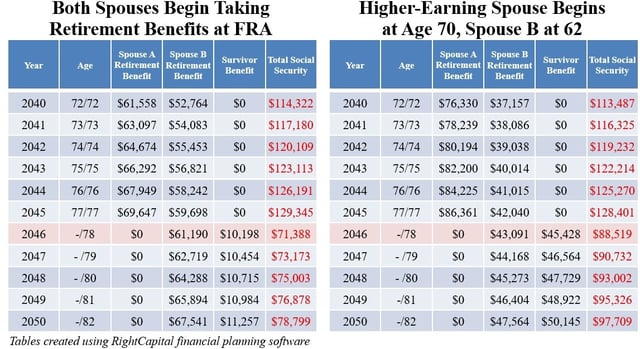
- Starting benefits at age 62 incurs a permanent reduction, full retirement age (66–67) delivers 100%, and each year of delay up to age 70 increases payments by about 8%.
- Adding wage-earning years, including part-time work, can replace zero-value years to raise the benefit calculation before filing.
- Coordinating Social Security claims with IRA or 401(k) withdrawals helps manage income taxes, which may affect up to 85% of your benefits.