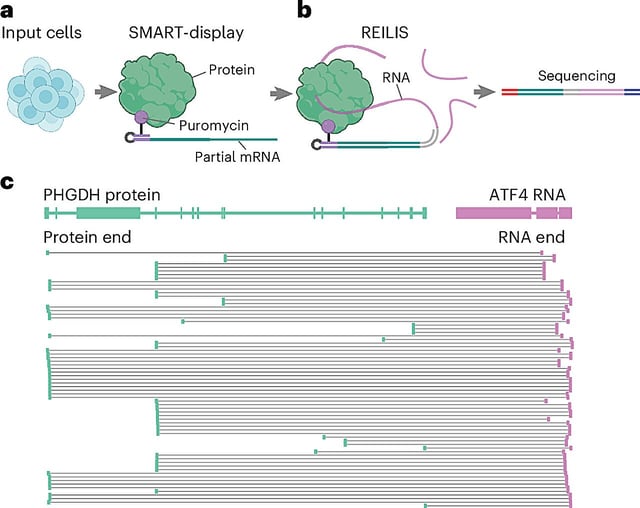
Overview
- PRIM‑seq freezes in‑cell RNA–protein contacts, tags proteins, and converts pairs into DNA barcodes readable by sequencing.
- Applied to two human cell lines, the approach generated the HuRPA resource with over 350,000 associations across roughly 7,000 RNAs and 11,000 proteins.
- The team verified known RNA‑binding proteins and identified unexpected interactors, including PHGDH binding mRNAs linked to survival and nerve growth.
- Researchers flagged LINC00339 as a high‑degree RNA that engages 15 membrane proteins, with additional validations for SMC1A, SMC3 and RAD21.
- Authors plan to deploy PRIM‑seq in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s models to prioritize targets, while noting most newly mapped interactions still require functional validation.