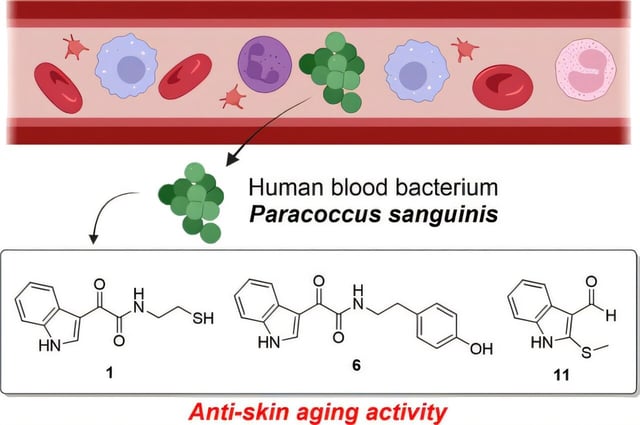
Overview
- Researchers isolated and structurally characterized twelve distinct indole-functionalized compounds produced by Paracoccus sanguinis.
- Three lead metabolites significantly lowered reactive oxygen species in treated human skin cells.
- The same three compounds also suppressed inflammatory proteins and inhibited collagenase activity in vitro.
- Two of the top anti-aging candidates were newly identified in this study, highlighting unexplored microbial chemistry.
- The research team will next evaluate the safety, bioavailability and efficacy of these metabolites in human clinical studies.