Overview
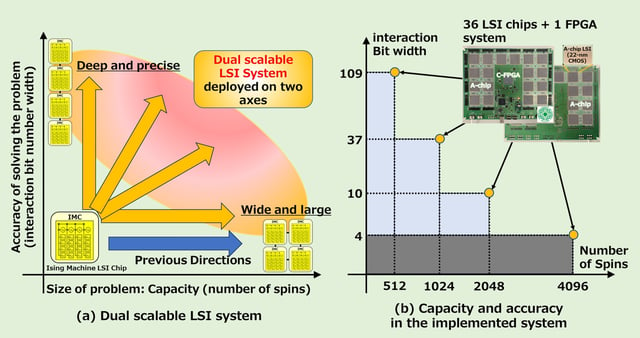
- The Dual Scalable Annealing Processing System (DSAPS), developed by Tokyo University of Science, simultaneously scales spin numbers and interaction bit widths, overcoming key limitations of traditional ASICs.
- Two prototype configurations—2048 spins with 10-bit interactions and 1024 spins with 37-bit interactions—showcase DSAPS's flexibility and precision.
- Validation tests achieved over 99% accuracy in MAX-CUT problems, with the 37-bit configuration reducing deviation to 0.73% in 0-1 knapsack tests, a significant improvement over the 10-bit model.
- DSAPS employs advanced ∆E block manipulation for dual scalability, combining high-capacity and high-precision structures to enhance computational efficiency.
- Starting in 2025, DSAPS will be integrated into the third-year electrical engineering curriculum at Tokyo University of Science, fostering hands-on learning in semiconductor design and optimization.