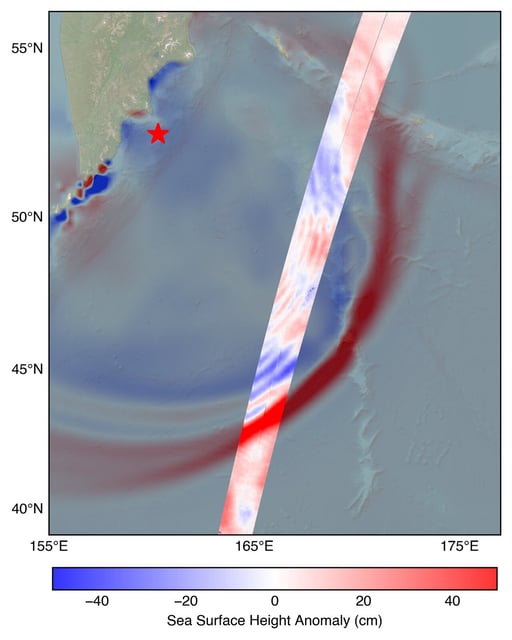
Overview
- On July 30 the NASA-CNES SWOT satellite captured the leading edge of a tsunami from an M8.8 Kamchatka earthquake, recording sea surface heights above 1.5 feet about 70 minutes after the quake struck.
- SWOT’s multidimensional measurements of wave height, shape and travel direction were plotted against a NOAA Center for Tsunami Research forecast and confirmed the model’s accuracy.
- The NOAA Center for Tsunami Research has initiated integration of SWOT-derived observations into its operational forecasting system to sharpen early-warning capabilities.
- SWOT’s Ka-band radar interferometer fills observational gaps by mapping open-ocean tsunami characteristics over broad swaths between coastal sensors.
- The joint mission led by NASA and CNES, with contributions from the Canadian and UK space agencies, demonstrates international cooperation to advance coastal hazard preparedness.