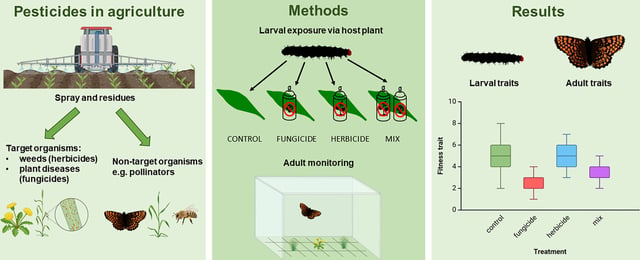
Overview
- The study found that a fungicide significantly increased larval mortality and delayed development in the Glanville fritillary butterfly, even after short-term exposure.
- Exposure to a mixture of fungicide and herbicide partially mitigated developmental delays caused by the fungicide but still resulted in sublethal stress and reduced reproductive success.
- Researchers emphasized the need for expanded environmental risk assessments that account for mixture toxicity and life-stage vulnerabilities in non-target species.
- Current EU regulations do not systematically monitor pesticide residues in terrestrial habitats, leaving wildlife exposure levels poorly understood.
- The findings call for improved pesticide monitoring, legislative reforms, and integration of biodiversity conservation into agricultural practices to address hidden threats to ecosystem health.