Overview
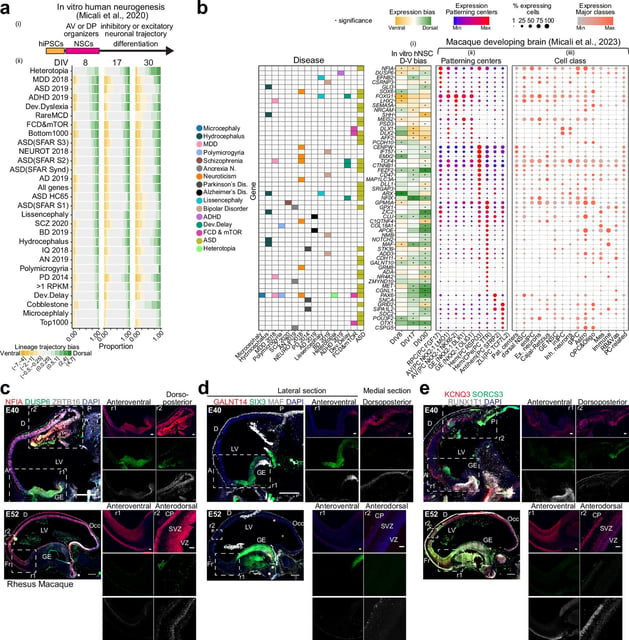
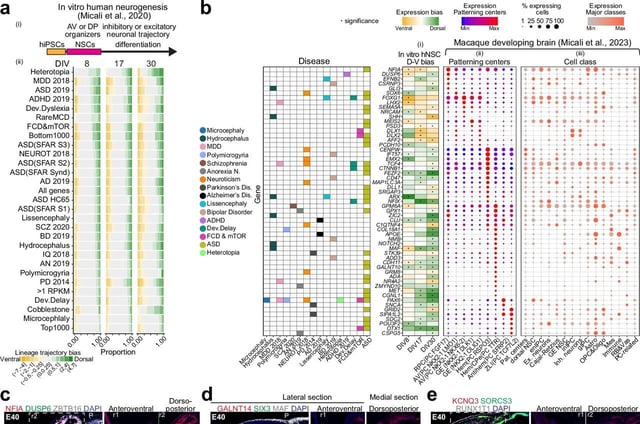
- Genes linked to autism, schizophrenia, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and other disorders are active in the earliest phases of fetal neural stem cell development.
- The team combined human and mouse brain datasets with in vitro stem cell models to simulate the effects of nearly 3,000 risk genes implicated in neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Analysis mapped specific developmental windows and cell types where genetic disruptions most significantly impair brain formation.
- The identified risk genes cover a wide range of conditions from cortical malformations like microcephaly and hydrocephaly to mood and movement disorders.
- These findings establish foundational targets for early, gene-focused therapies and personalized interventions to prevent lifelong brain disorders.