Overview
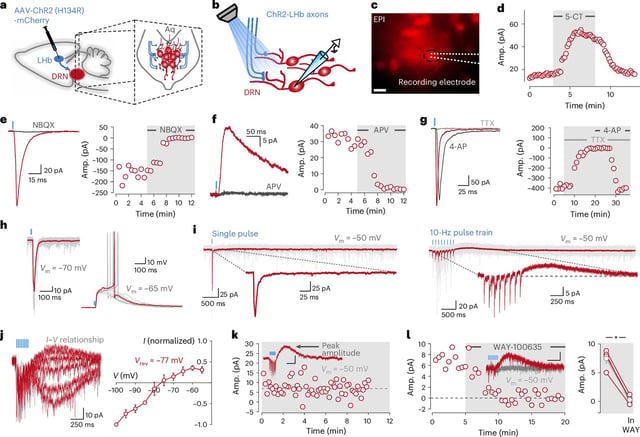
- Researchers discovered that serotonin neurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus form recurrent inhibitory networks, refuting the traditional model of independent activity.
- These networks implement winner-takes-all computations, where active neuron groups suppress less active ones, dynamically regulating serotonin release.
- Inputs from the lateral habenula modulate these networks, linking environmental threat signals to binary 'go' or 'don’t go' decisions.
- The findings reveal distinct subgroups of serotonin neurons that control region-specific serotonin release, highlighting functional heterogeneity.
- Future research will focus on testing these computational principles in naturalistic mouse behaviors, with potential implications for mood disorder therapies.