Overview
- The study recorded sleep brain activity of 40 healthy adults using AI-driven analysis and electroencephalography to compare caffeine and placebo nights.
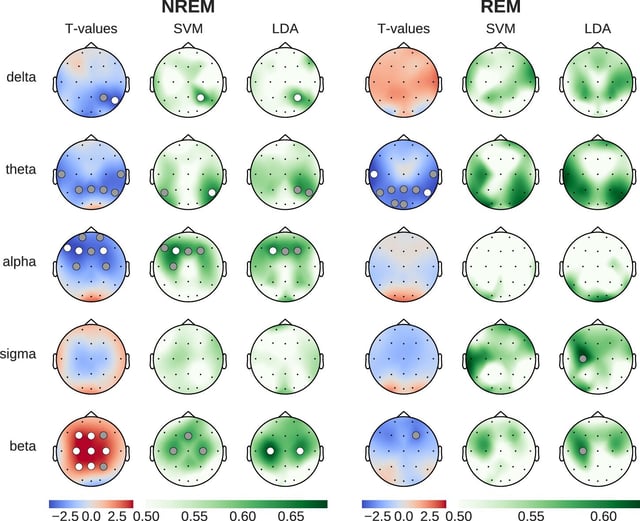
- Caffeine consumed before bedtime increased brain signal complexity and pushed neural activity toward a critical state of heightened alertness.
- Under the influence of caffeine, slower theta and alpha oscillations tied to deep restorative sleep were reduced while beta wave activity increased.
- Participants aged 20–27 exhibited stronger neural changes than those aged 41–58, likely due to higher adenosine receptor density in younger brains.
- Researchers caution that these alterations could impair overnight recovery and recommend further investigation into their effects on memory and cognitive health.