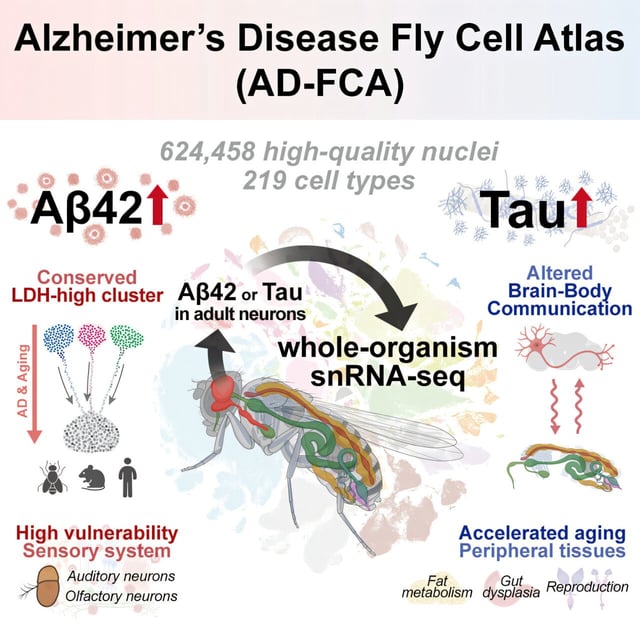
Overview
- Researchers created an Alzheimer’s Disease Fly Cell Atlas profiling 219 cell types to study whole-body impacts of Alzheimer’s proteins.
- Aβ42 expression in neurons primarily damages sensory neurons, impairing vision, hearing, and smell pathways.
- Tau expression in neurons disrupts fat metabolism, digestion, and reproduction, mimicking accelerated aging in peripheral tissues.
- The study highlights impaired brain-body communication as a key factor in Alzheimer’s systemic effects.
- Published in Neuron, the findings pave the way for identifying systemic biomarkers and developing holistic Alzheimer’s therapies.