Overview
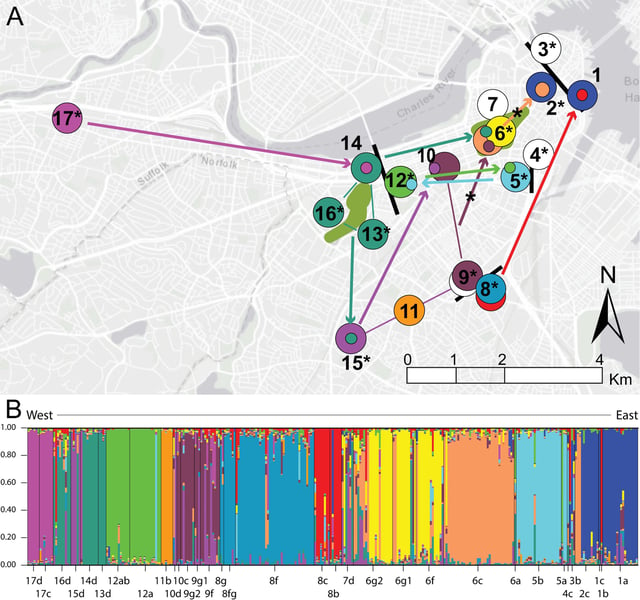
- A six-year study revealed stable, localized Leptospira strains in distinct Boston rat populations, with minimal variation over time.
- Researchers confirmed a genomic link between a 2018 human leptospirosis case and bacterial strains found in local rats.
- Urban infrastructure, such as multi-lane roads and greenways, shapes rat migration and influences the spread of Leptospira bacteria.
- Novel culturing and genomic sequencing techniques enabled the isolation and detailed analysis of bacterial strains from rat kidney samples.
- The findings underscore gaps in leptospirosis surveillance and the need for targeted pest control strategies to mitigate human health risks.