Overview
- Peer-reviewed results in Science Advances report that higher musicality aligns with stronger neural markers of top-down attention and weaker bottom-up distraction.
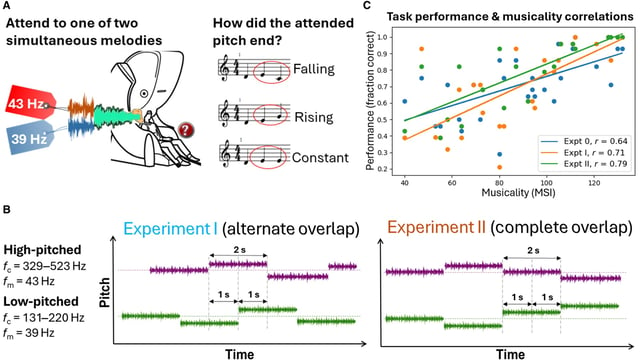
- Participants listened to two simultaneous melodies and tracked pitch changes in one, enabling stimulus-specific measurement of brain activity.
- The approach combined frequency tagging and machine learning to separate overlapping neural signals with high precision.
- Two magnetoencephalography experiments (n=28 and n=20) underpinned the findings, which the authors stress are correlational rather than proof of training-caused effects.
- The Karolinska–MIT collaboration, funded by the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation and the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research, declared no conflicts and noted potential uses in education and rehabilitation.