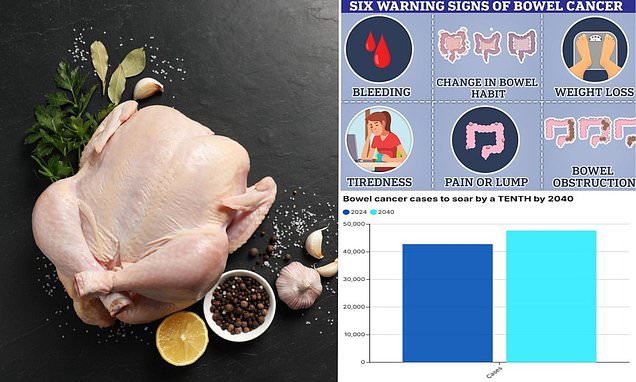
Overview
- A 19-year Italian cohort study published in Nutrients associates consuming over 300g of poultry weekly with a two-fold increase in gastrointestinal cancer mortality.
- Men face a 161% higher risk of gastrointestinal cancer-related death compared to women when consuming high levels of poultry.
- Researchers propose high-temperature cooking, feed treatments, and hormone residues in poultry may contribute to cancer risks but call for further investigation to confirm these mechanisms.
- The study suggests moderating poultry intake, alternating protein sources like fish, and adopting safer cooking methods to reduce potential health risks.
- Limitations of the study include a lack of data on cooking practices, processing methods, and participants' physical activity, which may affect causality conclusions.