Overview
- A new study suggests firefighters may face a heightened risk of gliomas, a type of brain cancer, due to exposure to haloalkanes found in flame retardants and fire extinguishers.
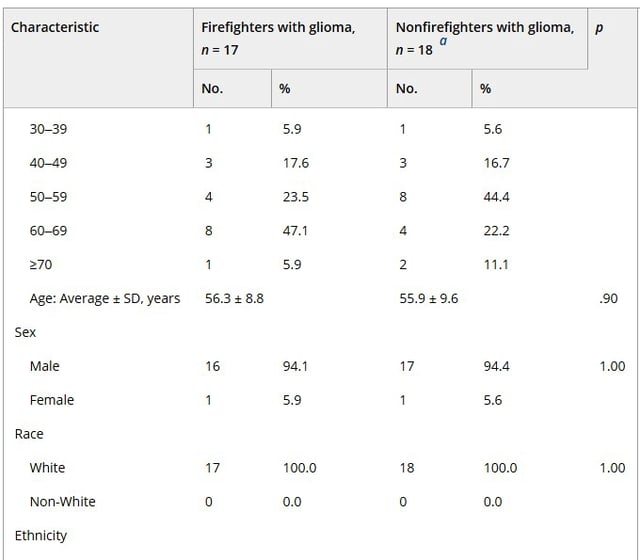
- Researchers identified mutational signatures linked to haloalkane exposure in tumors from 17 firefighters and 18 non-firefighters, with higher prevalence in firefighters.
- The study, published in the journal *Cancer*, highlights the need for further research with larger sample sizes to confirm these preliminary findings.
- Non-firefighters with similar mutations were often exposed to haloalkanes through occupations such as painting or auto mechanics.
- Experts stress that understanding exposure-related genetic mutations could inform public health strategies to mitigate risks for firefighters and other affected groups.