Overview
- The study, published in BMJ Open, analyzed data from eight observational studies involving 301,533 participants.
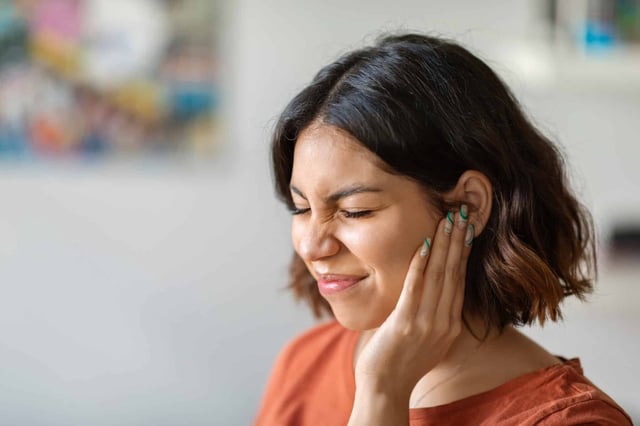
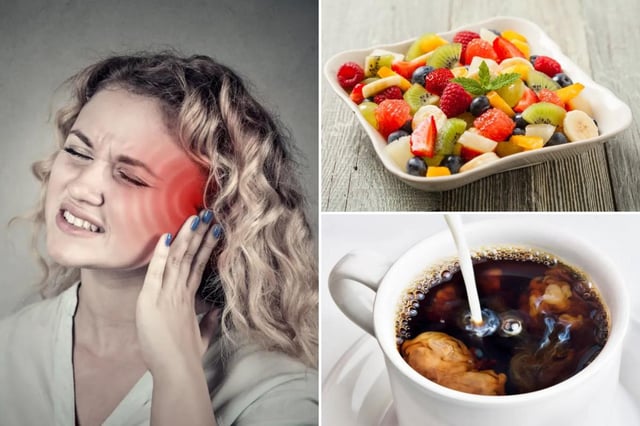
- Higher fruit intake was associated with a 35% reduction in tinnitus risk, while dairy consumption showed a 17% reduction.
- Caffeine intake was linked to a 10% lower risk, though findings on its effects remain contentious, and dietary fiber showed a 9% reduction in risk.
- Researchers suggest potential mechanisms include antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects on blood vessels and nerves.
- Experts caution that the evidence is observational and of low quality, calling for large-scale, well-designed studies to confirm these findings.