Overview
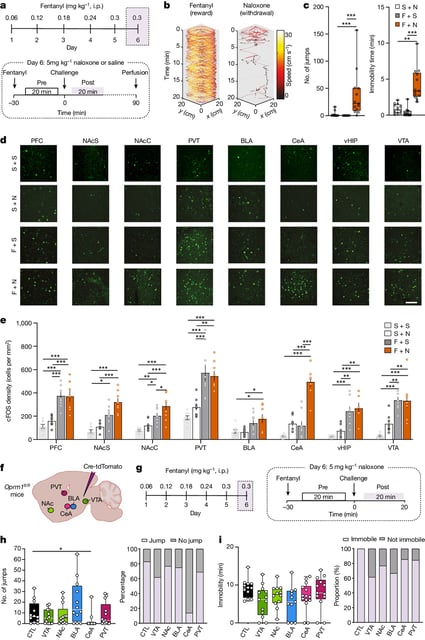
- Researchers identified two neural pathways responsible for fentanyl's addictive properties and withdrawal symptoms.
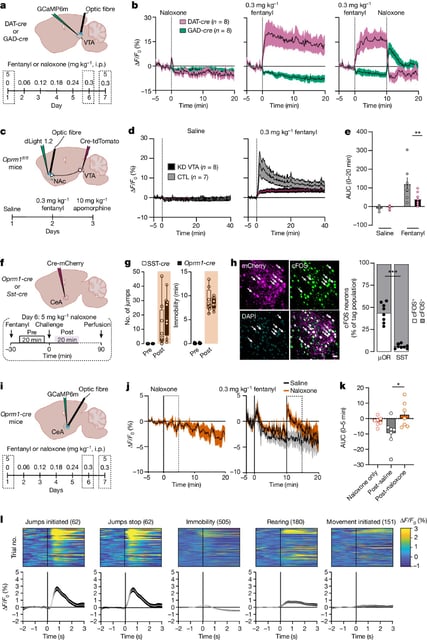
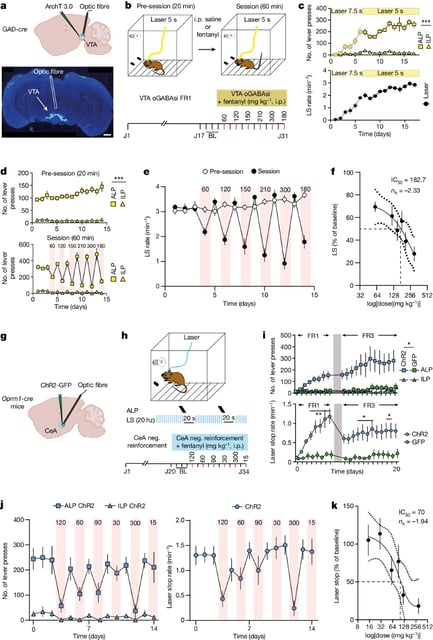
- The study showed that dopamine-releasing neurons in the VTA are linked to the drug's rewarding effects.
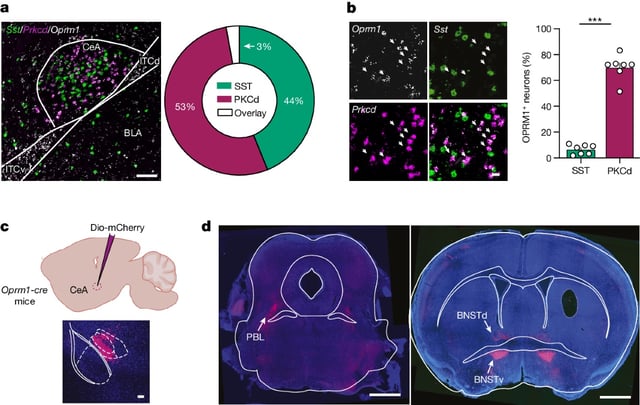
- Withdrawal symptoms are associated with increased activity in neurons in the central amygdala.
- Genetically engineered mice could turn off neurons linked to withdrawal, indicating a potential target for therapy.
- Further research is needed to see if these mechanisms are present in humans and how they interact.