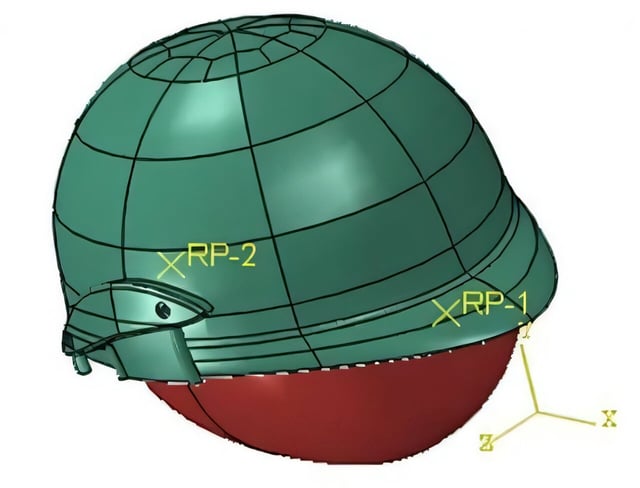
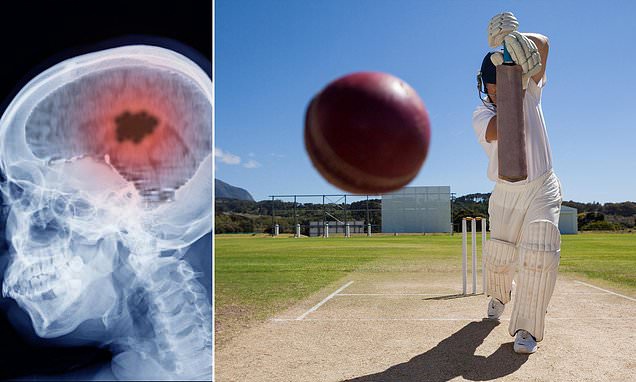
Overview
- Computational models combined precise helmet geometries with cranial structures to track stress and strain distribution in ABS, fiberglass alloy and aluminum composite helmets under cricket-specific impacts.
- Researchers determined that ABS helmets offer adequate protection for training and recreational play, while elite cricketers benefit from the higher-energy absorption of fiberglass or aluminum composite headgear.
- Aluminum composites achieved the most uniform stress distribution across the head’s surface despite greater brittleness, and fiberglass alloys similarly reduced peak brain-tissue stress through even load dispersion.
- With cricket balls averaging speeds of around 80 mph and elite players facing head-related injuries in up to 70% of cases, optimized helmet materials are crucial to mitigating traumatic brain injury risks.
- Study authors stress that these findings apply solely to cricket’s unique loading conditions and call for sport-specific helmet evaluations to address varying impact scenarios.