Overview
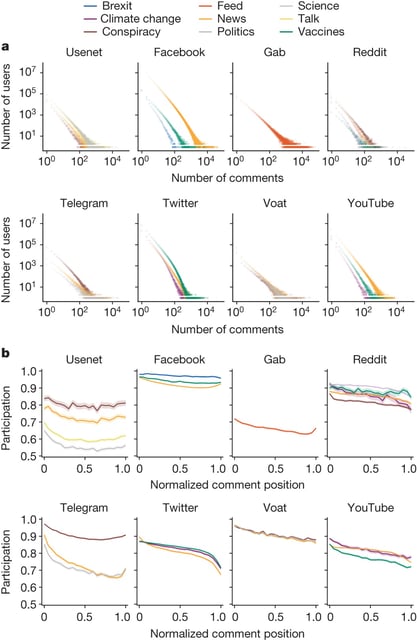
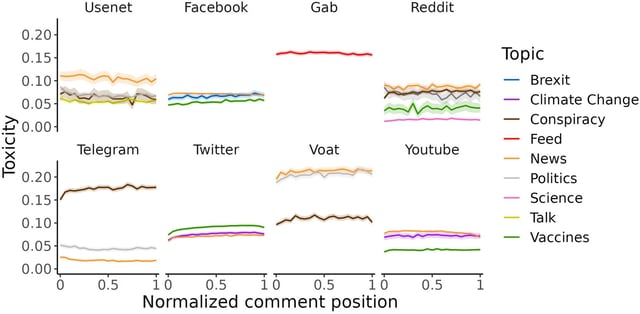
- A comprehensive study analyzing over 500 million threads across eight platforms over 34 years finds that human behavior is the primary driver of online toxicity.
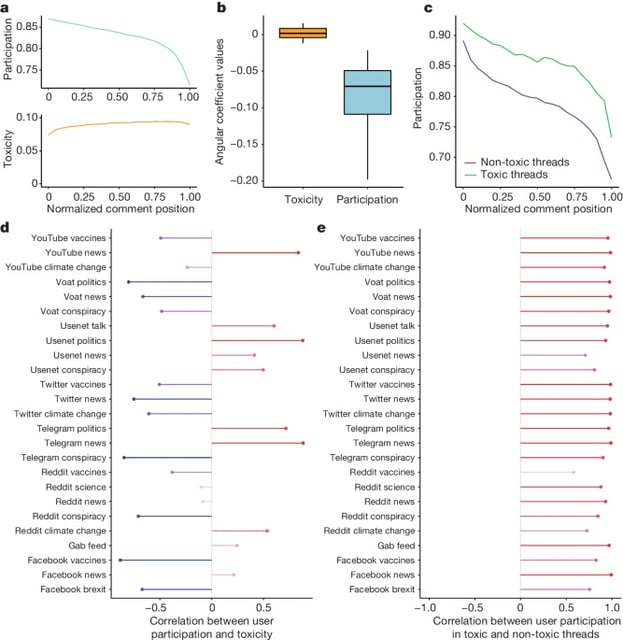
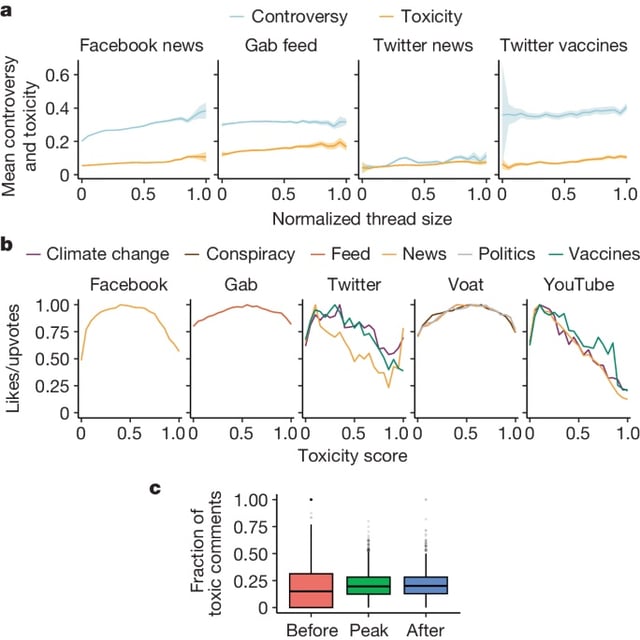
- Toxicity does not deter users from social media; engagement patterns in toxic and non-toxic conversations are nearly identical.
- The study challenges the common belief that social media platforms and algorithms are the main contributors to online toxicity.
- Polarization and diverse opinions contribute more to hostile online discussions than toxicity itself, reinforcing platform participation.
- The research suggests that content moderation and cognitive media training can reduce online toxicity by addressing human behavior.