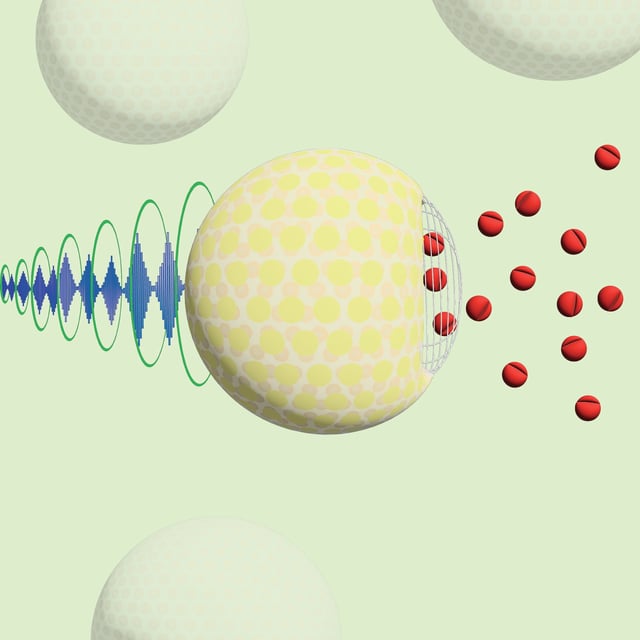
Overview
- In rat experiments, focused ultrasound targeting the medial prefrontal cortex delivered about three times more ketamine to that region and produced measurable reductions in anxious behavior.
- A 2.5-minute ultrasound session to the sciatic nerve released encapsulated ropivacaine, inducing localized anesthesia for over an hour without systemic effects.
- The nanoparticles feature a 5 percent sucrose core and phospholipid shell—leveraging mRNA vaccine–grade liposome technology to enhance stability and drug loading.
- Encapsulation significantly lowered off-target ketamine concentrations across organs including liver, kidney and heart compared with equivalent free-drug injections.
- Researchers are refining particle design to further reduce drug leakage and elucidate the ultrasound-triggered release mechanism while preparing for FDA clearance of a ketamine trial in chronic pain patients.