Overview
- Epilepsy surgery success rates remain at 50–60% due to challenges in accurately identifying epileptogenic zones (EZs).
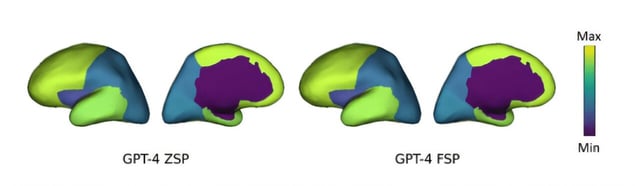
- ChatGPT matched or outperformed board-certified epileptologists in localizing common EZ regions like the frontal and temporal lobes.
- Human experts still outperformed ChatGPT in identifying EZs in rare regions such as the insula and cingulate cortex.
- Researchers introduced EpiSemoLLM, the first large language model fine-tuned for seizure semiology interpretation, hosted on a Stevens GPU server.
- The study highlights the potential of AI-human collaboration in improving preoperative assessments and surgical outcomes for epilepsy patients.