Overview
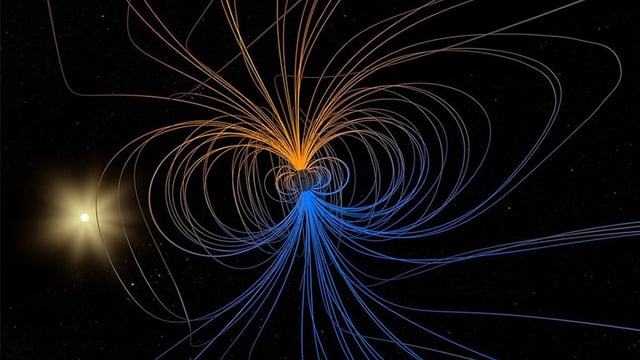
- GFZ researchers led by Sanja Panovska and Ahmed Nasser Mahgoub reconstructed a global model of Earth’s magnetic field during the Matuyama-Brunhes reversal using sediment drill-core data.
- An accompanying animation and audio track translate paleomagnetic readings into a soundscape that illustrates poles staggering, splitting into blobs and merging unpredictably.
- The project integrates isotopic markers such as beryllium-10 from ice cores to map fluctuations in field strength throughout the 780,000-year-old reversal.
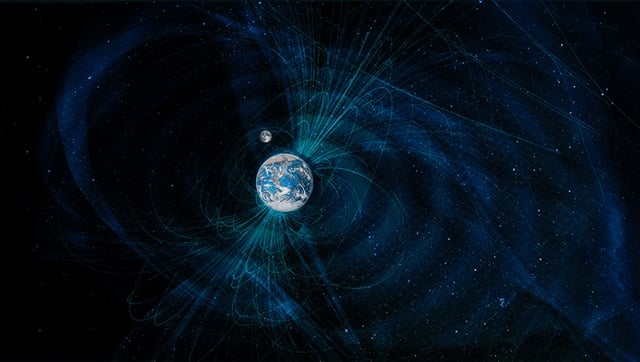
- Contemporary satellite and ground-based observations of magnetic pole drift and the South Atlantic Anomaly are compared with ancient anomaly patterns to assess current field stability.
- Geologist Andreas Nilsson forecasts that the South Atlantic Anomaly will dissipate within 300 years, effectively ruling out an imminent polarity flip.