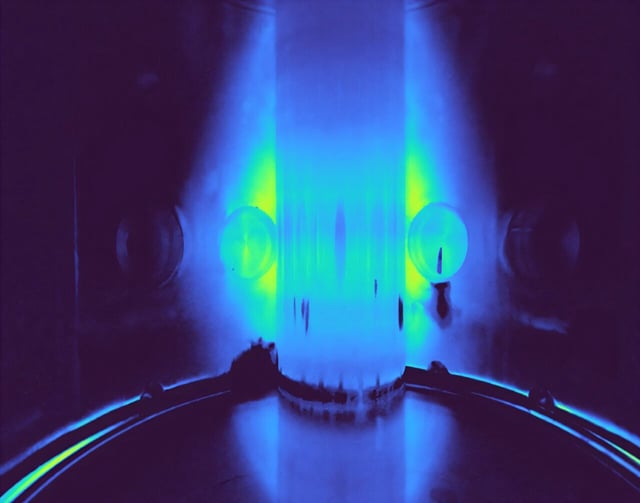
Overview
- SMART (SMall Aspect Ratio Tokamak) successfully generated its first tokamak plasma, a key step toward sustainable fusion energy.
- The device uses a novel negative triangularity plasma shape, which improves performance by suppressing damaging instabilities and enhancing heat distribution.
- Developed by the University of Seville, SMART is part of the Fusion2Grid strategy to create the most compact and efficient fusion power plant design.
- Researchers aim to establish the physics and engineering foundations for high-field spherical tokamaks with solenoid-driven plasma.
- The achievement has sparked global interest, with scientists anticipating advancements in compact fusion reactor capabilities.