Overview
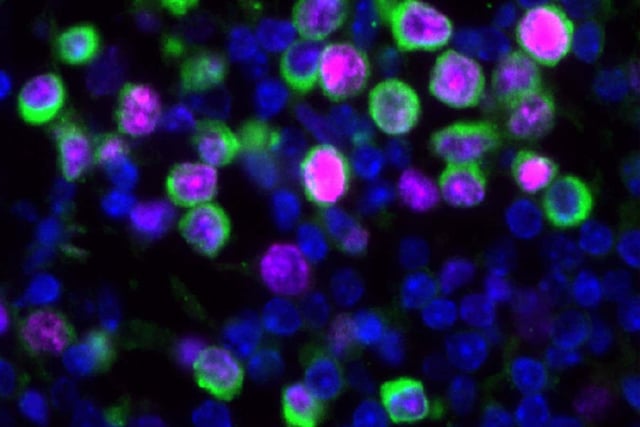
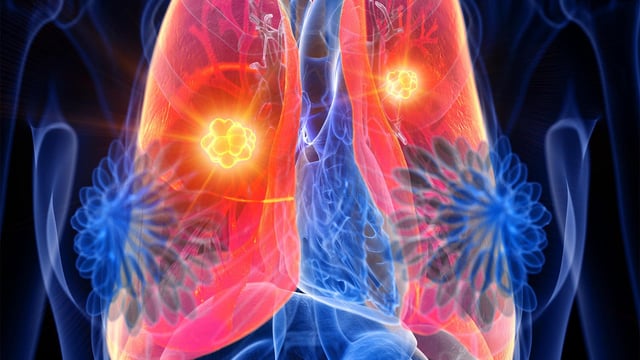
- Mouse experiments published in Nature show SARS-CoV-2 and influenza infections trigger IL-6–driven inflammation that awakens dormant breast cancer cells and drives rapid lung metastasis.
- Genetically engineered mice lacking IL-6 did not exhibit post-infection cancer cell proliferation, identifying the cytokine as essential for tumor reactivation.
- Reactivated cancer cells exploit helper T cells to shield themselves from cytotoxic T cell attack during metastatic growth following infection.
- Analyses of the UK Biobank and Flatiron Health databases reveal survivors with COVID-19 face nearly twice the risk of cancer-related death and a 50% higher incidence of lung metastases than uninfected peers.
- Researchers are exploring IL-6 inhibitors, reinforcing vaccination guidance for cancer survivors and planning broader clinical trials across cancer types and common respiratory pathogens.