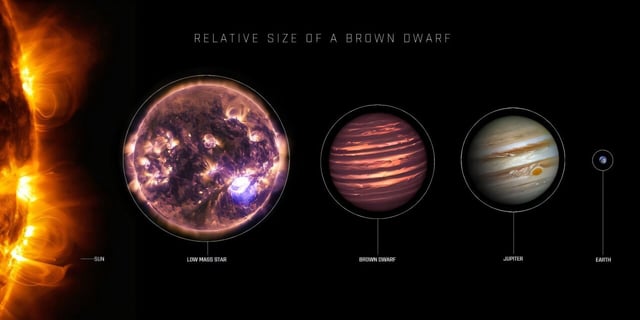
Overview
- The July 7 study in the Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics proposed that brown dwarfs in dark matter–rich regions could capture self-annihilating WIMPs to power stable “dark dwarfs.”
- Dark dwarfs are expected to preserve lithium-7, unlike conventional brown dwarfs that destroy it, providing a unique spectroscopic detection marker.
- Model calculations place dark dwarfs close to the Milky Way’s center, where dark matter density exceeds 10^3 GeV/cm³.
- Planned JWST infrared observations and ground-based spectroscopic surveys will search for cool substellar objects with anomalous lithium-7 levels near the galactic core.
- Detecting even one dark dwarf would strongly support the hypothesis that dark matter consists of heavy, self-interacting particles like WIMPs.