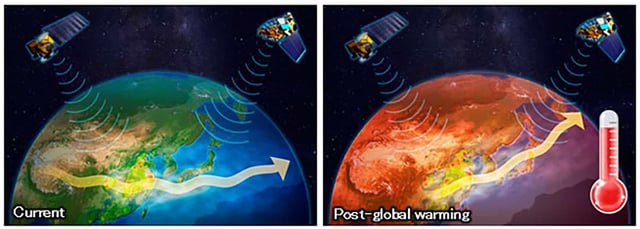
Overview
- The study uses aerosols as tracers to detect climate change effects on transboundary air pollution from China.
- Researchers analyzed 19 years of satellite data to develop a new metric called RAOD.
- Findings indicate seasonal shifts in aerosol pathways, with significant year-to-year variations.
- The new method offers a more accurate way to predict climate impacts compared to traditional models.
- The study underscores the potential for more severe climate impacts than currently predicted.