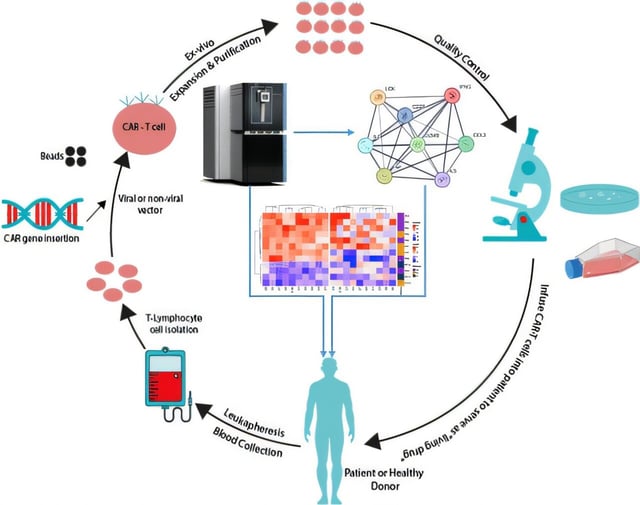
Overview
- Researchers at the Center for Cell-Based Therapy at the University of São Paulo employed proteomic profiling and advanced mass spectrometry to dissect CAR-T cell molecular mechanisms.
- The analysis uncovered 14 pivotal proteins across four functional groups: cytokines, kinases, receptors, and proteases/chemical messengers.
- Key molecules identified include interferon gamma, CCL3, LCK, ITK, CD80, CD20, Granzyme B, and TNF-α.
- Interferon gamma and interleukin-2 emerged as candidate surrogate biomarkers for monitoring and potentially enhancing patient response.
- The results provide a blueprint for refining CAR-T constructs to address therapy resistance and improve treatment durability in blood cancers.