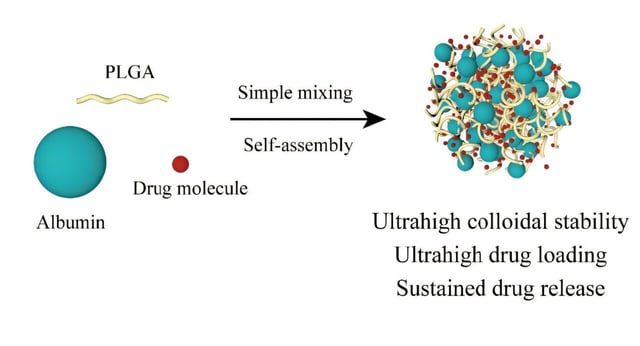
Overview
- The hybrid supraparticles form through coassembly of biodegradable PLGA polymer and natural albumin protein to leverage both sustained release and biocompatibility.
- The nanoparticles encapsulate up to 40% of the chemotherapy drug doxorubicin by weight, markedly surpassing commercial formulations such as Doxil.
- Under laboratory conditions, the particles remained physically and chemically stable for over six months without aggregation or drug leakage.
- In vitro and in vivo tests demonstrated effective drug delivery to cancer cells and animal tumors with minimal damage to healthy tissues.
- Preliminary scale-up experiments demonstrate reproducible production without compromising particle uniformity, and the team plans to adapt the platform for other therapeutic agents.