Overview
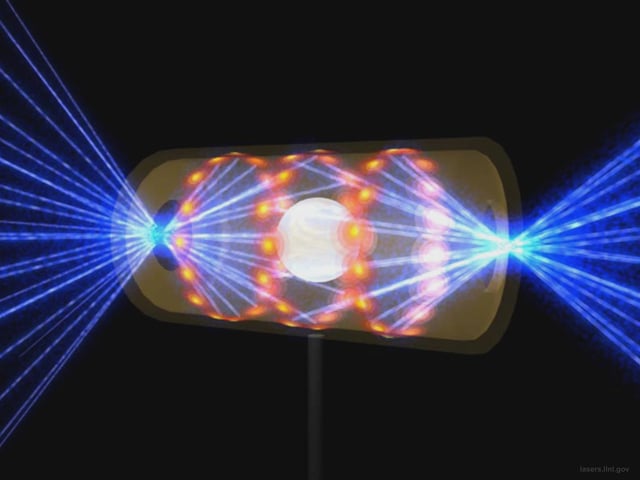
- A Science paper by Brian Spears and LLNL collaborators introduces a physics-informed generative AI model validated against NIF’s 2022 fusion ignition experiment.
- The model assigned a 70–74% probability to the successful ignition shot, marking an improvement from about 50% accuracy in earlier versions.
- Training incorporated NIF experimental results, high-fidelity radiation-hydrodynamics simulations, Bayesian analysis and subject-matter expertise with over 30 million CPU hours on supercomputers.
- By modeling real-world failure modes such as laser timing variability and target defects, the approach delivers more realistic predictions for inertial confinement fusion outcomes.
- Researchers highlight the model’s value in guiding future experimental design and resource allocation but note that commercial fusion power remains a longer-term challenge.