Overview
- ETH Zurich and Google unveiled Phoenix, a Rowhammer technique that uses self-correcting refresh synchronization to evade enhanced Target Row Refresh on DDR5.
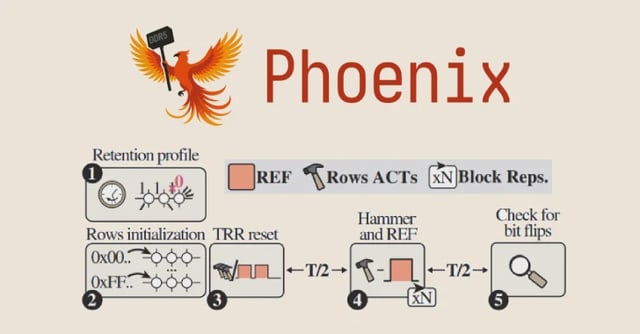
- In tests on SK Hynix modules, researchers induced bit flips on all 15 chips evaluated and achieved root on a default DDR5 desktop in as little as 109 seconds.
- The team reverse-engineered in-DRAM behavior with open-source FPGA-based platforms developed with Antmicro and published resources and proof-of-concept code.
- The work is tracked as CVE-2025-6202 with high severity, and evaluations showed practical impacts including page-table manipulation and cross-VM RSA key exposure.
- Raising the DRAM refresh rate to 3x blocked Phoenix in tests but may harm performance and stability, as industry efforts advance toward deterministic defenses such as PRAC.