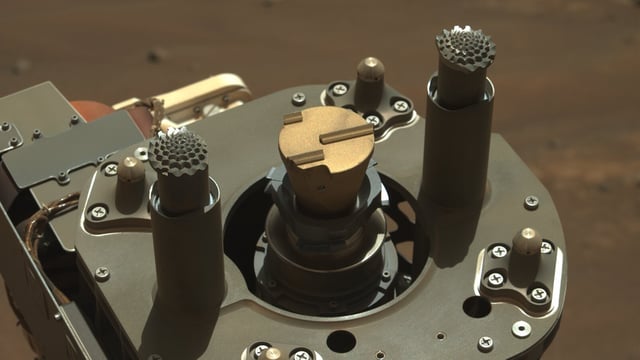
Overview
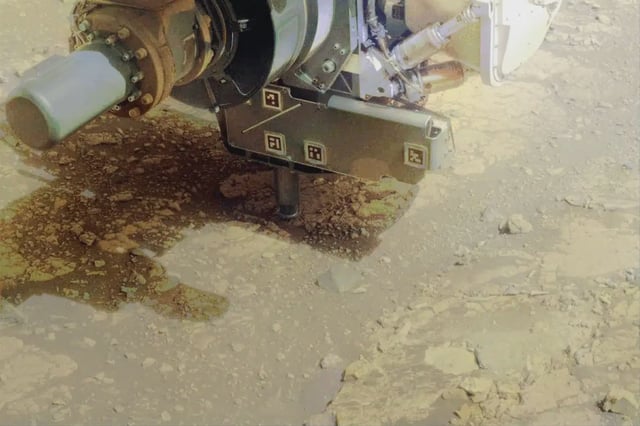
- On June 3, Perseverance ground down a rock nicknamed ‘Kenmore’ in Jezero Crater using its abrading bit and gDRT to expose fresh interior surfaces.
- SuperCam, SHERLOC and PIXL instruments detected clay minerals, feldspar and a manganese hydroxide in the abraded samples.
- The presence of water-bound hydroxide molecules in the clay deposits offers new insights into Mars’ ancient aqueous environments.
- On Sol 1540 (June 19, 2025), the rover drove 411 meters in a single AutoNav session, breaking its previous autonomous distance record.
- Data from the ‘Kenmore’ analysis and extended self-driving tests will guide future Mars exploration strategies for sampling and navigation.