Overview
- Physical Review Letters published the study, titled “Novel Approach to Cosmological Nonlinearities as an Effective Fluid,” on August 15, 2025.
- The approach treats nonlinear cosmic structure as an effective fluid to compute its impact on measurements without invoking new physics, according to the authors.
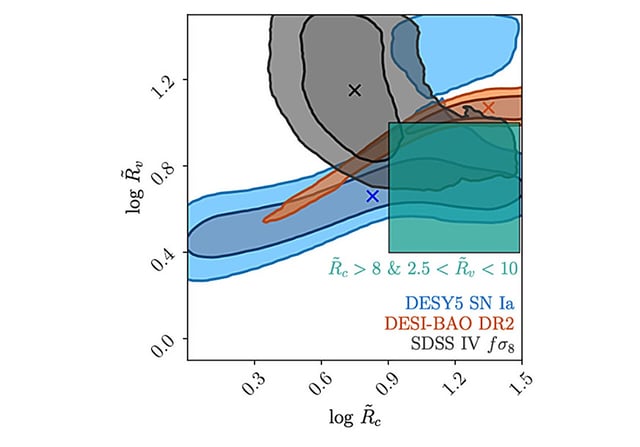
- Using DESI and other independent datasets, the team identified minimum influential scales R_v for voids and R_c for clusters that can alter cosmological inference.
- Dataset contours overlapped in a region indicating large voids may underlie observed anomalies, and the authors highlight a plotted green box where their model resolves the Hubble tension.
- The authors also argue the framework can account for apparent dynamical dark energy signals, a claim that now requires reproduction and further observational tests.