Overview
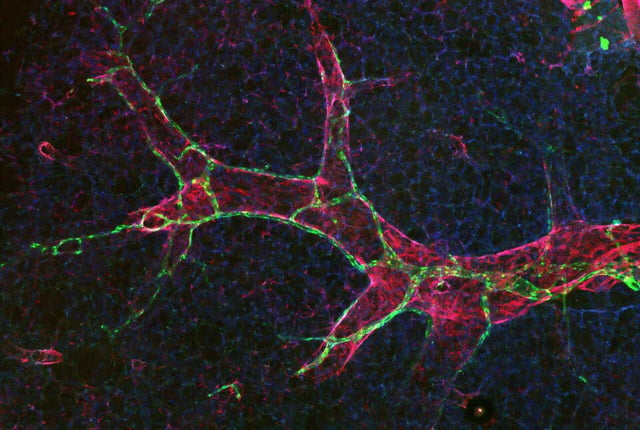
- Published July 17 in Nature Cardiovascular Research, the study revealed that PAR1 activation converts tight zipper junctions into permeable button junctions in lung lymphatic endothelial cells.
- In mouse lung models, loss of PAR1 prevented the zipper-to-button transition during inflammation, reducing fluid drainage and causing immune cell accumulation.
- Lymphatic vessels responded positively to PAR1 signals by enhancing permeability for healing, in contrast to blood vessels where similar activation leads to pathological leakage.
- Findings suggest that broad PAR1 inhibitors used in cardiovascular and cancer trials could inadvertently impair lymphatic-mediated lung recovery.
- Research teams are now developing methods to selectively modulate PAR1 in lymphatic vessels and testing the effects on infection-driven lung injury.