Overview
- The study presented at ESCMID Global 2025 confirms over 3 million pediatric deaths globally in 2022 due to antimicrobial resistance (AMR)-related infections.
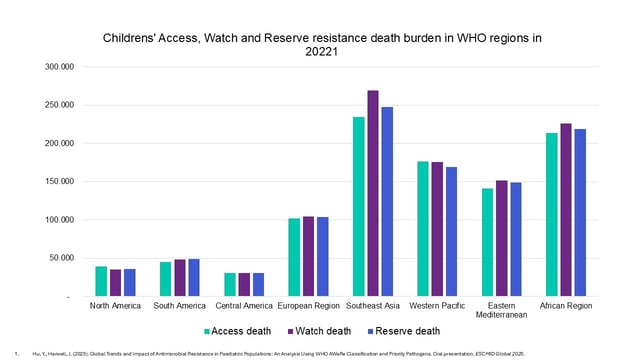
- Southeast Asia and Africa were the hardest-hit regions, with over 752,000 and 659,000 child deaths, respectively, linked to AMR complications.
- Approximately 2 million deaths were associated with the misuse of Watch and Reserve antibiotics, which are intended for limited use to prevent resistance development.
- Between 2019 and 2021, the use of Watch antibiotics surged by 160% in Southeast Asia and 126% in Africa, while Reserve antibiotic use rose by 125% in Africa alone.
- Experts call for urgent global action, including improved surveillance, mandatory pediatric antimicrobial stewardship programs, and regional policy reforms to curb AMR's impact.