Overview
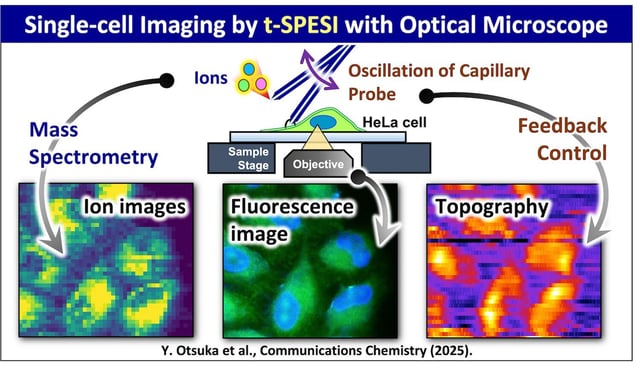
- Scientists at the University of Osaka have introduced a t-SPESI platform that allows high-resolution visualization of molecular distributions within individual cells.
- The system integrates tapping-mode scanning probe electrospray ionization (t-SPESI) with an inverted fluorescence microscope for multimodal imaging.
- Initial experiments on HeLa cells demonstrated the ability to map lipid distributions and distinguish cell types based on lipid profiles and surface morphology.
- The breakthrough, published in *Communications Chemistry*, establishes the method’s scientific rigor and potential for broader adoption in biomedical research.
- This innovation could advance precision medicine by identifying cellular subpopulations and biomarkers for targeted diagnostics and therapies.