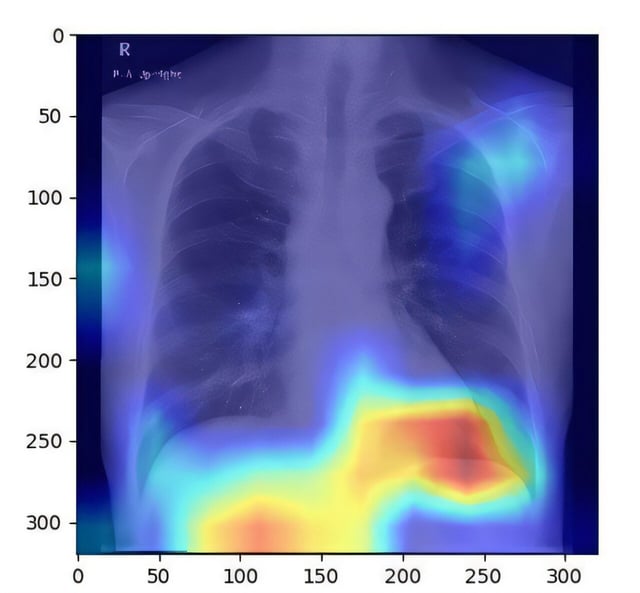
Overview
- The model was developed by Associate Professors Sawako Uchida-Kobayashi and Daiju Ueda at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Medicine.
- Researchers trained the deep learning algorithm on 6,599 chest X-ray images from 4,414 patients, using controlled attenuation parameter scores as ground truth measures of liver fat.
- It achieved an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve between 0.82 and 0.83, demonstrating reliable differentiation between patients with and without fatty liver disease.
- Leveraging standard chest radiographs capitalizes on their widespread availability, low cost and reduced radiation compared with ultrasound, CT and MRI.
- Published in Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging, the findings pave the way for prospective validation and integration of the tool into clinical workflows for early disease detection.