Overview
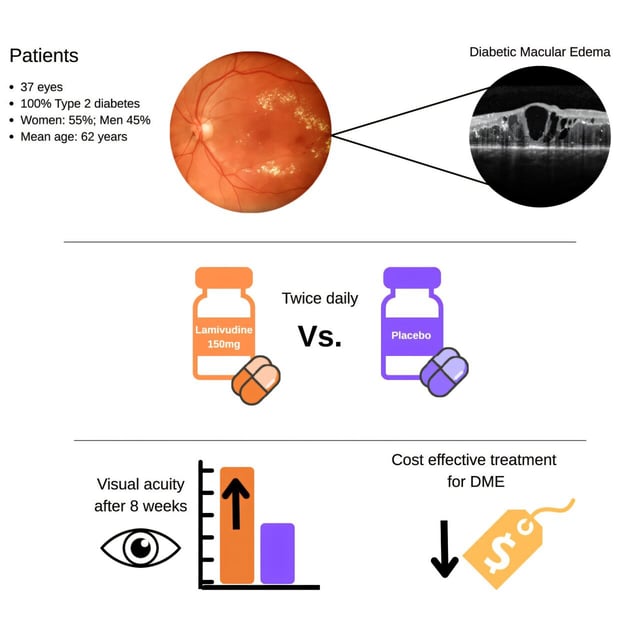
- In a randomized trial of 24 adults, those receiving lamivudine for four weeks gained an average of 9.8 letters on standardized eye charts before any injections
- After subsequent bevacizumab injections, lamivudine-treated patients improved by 16.9 letters compared with a 5.3-letter gain in the placebo group
- Lamivudine works by blocking inflammasomes, offering a distinct mechanism from current anti-VEGF therapies
- At about $20 per month, the oral therapy could dramatically reduce costs versus intravitreal injections that run up to $2,000 monthly
- Plans for larger, longer clinical trials are underway alongside development of K9, a lamivudine derivative designed to block inflammasomes with fewer side effects