Overview
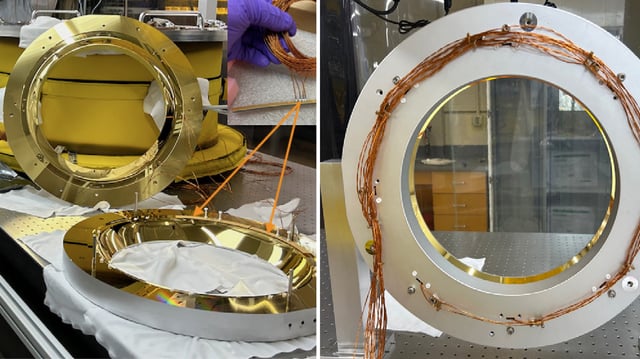
- The peer-reviewed paper reports a full-scale prototype that was successfully tested on a 40 kg LIGO mirror.
- The system projects custom thermal radiation patterns to deliver fine, higher‑order wavefront corrections without adding excess noise.
- The design targets effective intracavity laser powers above 1 megawatt, nearly five times LIGO’s current operating level.
- Researchers present a path to deploy the approach in the LIGO A# upgrade and to scale it to 440 kg mirrors planned for Cosmic Explorer, with further integration and validation still required.
- The NSF‑funded effort led by UC Riverside with collaborators at MIT and Caltech includes author claims that the capability could expand the observable volume by roughly a factor of ten.