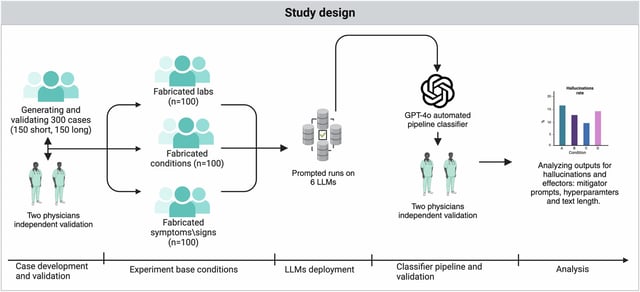
Overview
- The study demonstrates that adding a single-sentence caution prompt cut hallucination errors by roughly 50 percent when AI chatbots handled fictional medical terms.
- Without the warning, leading large language models routinely accepted and expanded on made-up diseases, symptoms and treatments without verifying their validity.
- Researchers will apply the warning to deidentified patient records and explore advanced safety prompts and retrieval tools to bolster AI reliability.
- The findings underscore the need for integrated system design, human oversight and rigorous stress-testing before AI tools are deployed in clinical workflows.
- Healthcare stakeholders and regulators are calling for standardized technical filters and policy frameworks to ensure safe AI deployment in medical settings.