Overview
- NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center projects a minor G1 geomagnetic storm on July 27 with isolated moderate G2 periods and a peak Kp index of 5 around 09:00–12:00 UTC.
- The disturbance stems from a coronal mass ejection launched on July 23 that is expected to interact with Earth’s magnetic field.
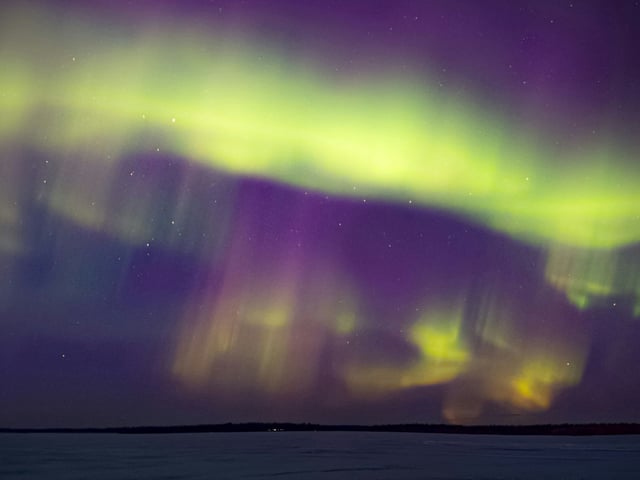
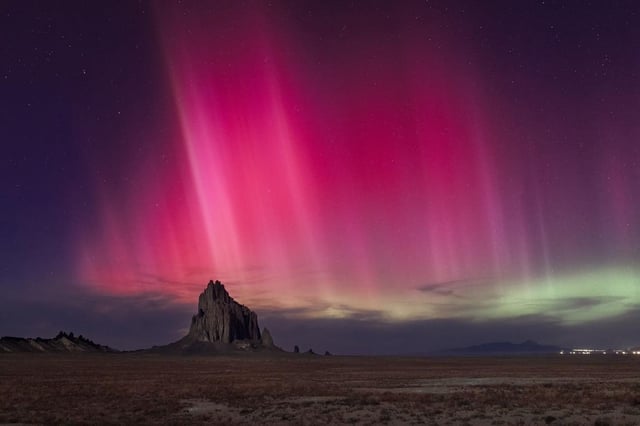
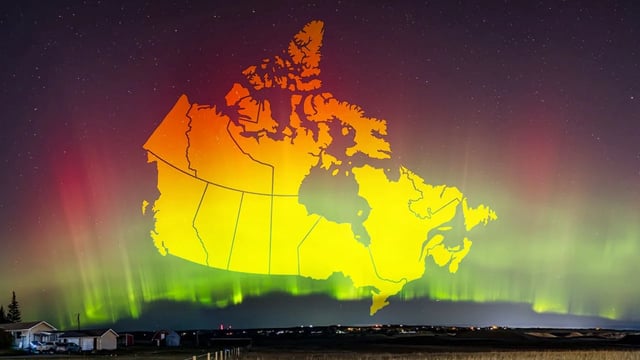
- Aurora visibility may reach 14 northern U.S. states—from Washington through Maine—and span most of Canada, including southern Ontario and British Columbia.
- Optimal viewing windows run from 10 p.m. to 2 a.m. local time under dark, clear skies with minimal light pollution on the northern horizon.
- Magnetic activity remains elevated following the October 2024 solar maximum peak, sustaining strong aurora potential through 2026.