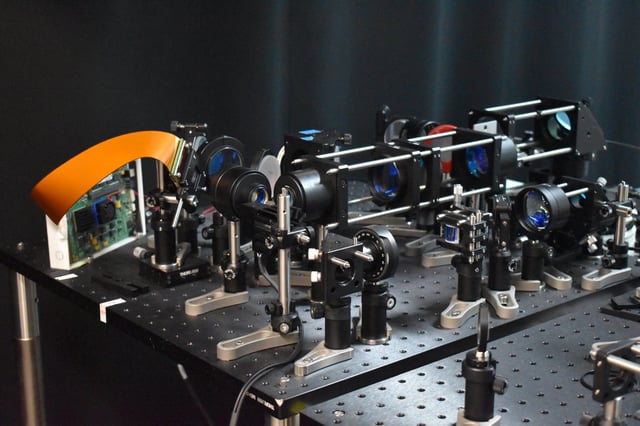
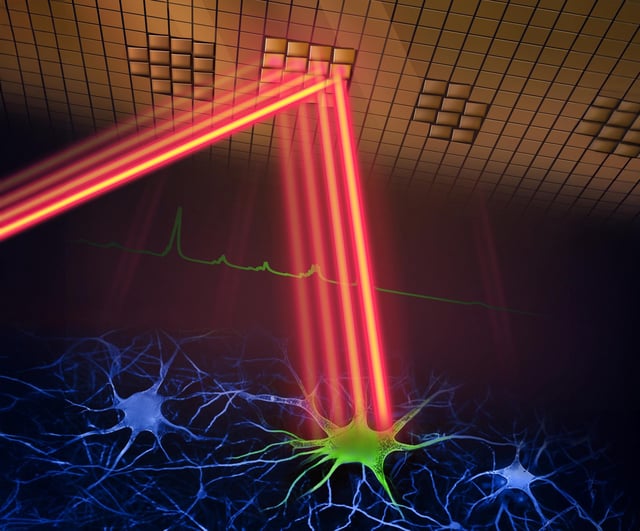
Overview
- The microscope captures high-speed images of neural activity at cellular resolution, significantly faster than traditional methods.
- Adaptive sampling and line illumination reduce laser power, minimizing damage to brain tissue.
- Researchers can now observe real-time neural dynamics, crucial for understanding learning, memory, and decision-making.
- The technology holds potential for early-stage study and treatment of neurological diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
- Future enhancements aim to integrate voltage imaging and improve the microscope's usability and size.