Overview
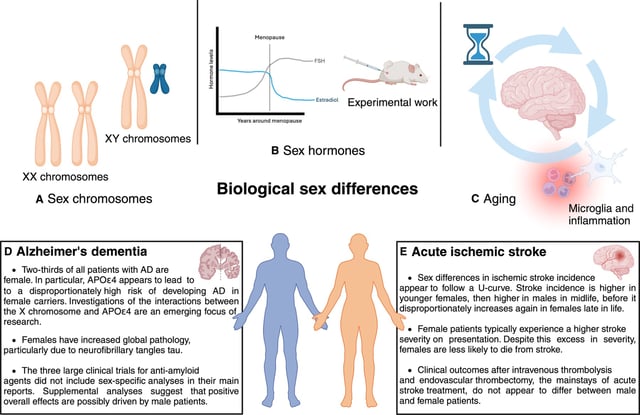
- Women face twice the risk of Alzheimer’s compared to men, with nearly two-thirds of cases occurring in females.
- Differences in X chromosome gene dosage affecting immune function and brain structure may contribute to women’s elevated vulnerability.
- The drop in estrogen levels during menopause is identified as a key driver of increased Alzheimer’s risk among women.
- Hormone replacement therapy initiated after age 70 has been associated with higher tau protein accumulation and accelerated cognitive decline.
- Researchers are designing longitudinal studies to monitor menopause timing, blood biomarkers, brain imaging and cognition to uncover mechanisms behind the gender gap.