Overview
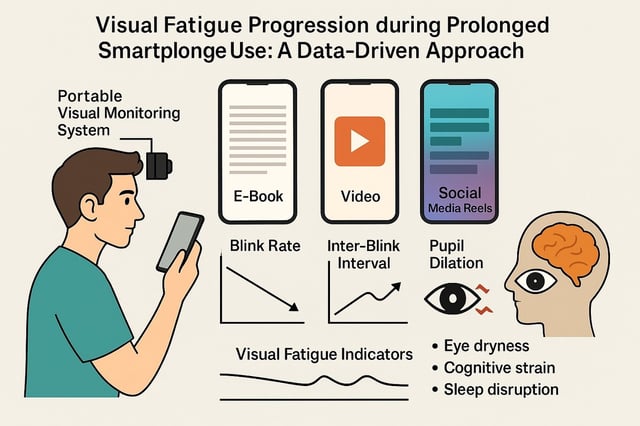
- The peer-reviewed Journal of Eye Movement Research study monitored 30 young adults during one-hour sessions of e-book reading, video watching and social-media reels using a portable eye-tracking system.
- Scrolling short-form reels produced the greatest strain, with larger pupil fluctuations than reading or watching videos.
- Across tasks, blink rate fell by about 54–61 percent and inter-blink intervals lengthened by 39–42 percent, objective markers of visual fatigue.
- Heavy usage remains widespread, with Americans averaging 5 hours and 16 minutes on their phones daily and nearly 7 in 10 reporting phone-related health issues, including eye strain for more than 4 in 10.
- Clinicians warn increased near work aligns with rising myopia—which raises risks such as retinal detachment—and advise the 20-20-20 rule, ergonomic setups, active blinking, lubricating drops, regular exams and treating dry eye before refractive or cataract surgery.