Overview
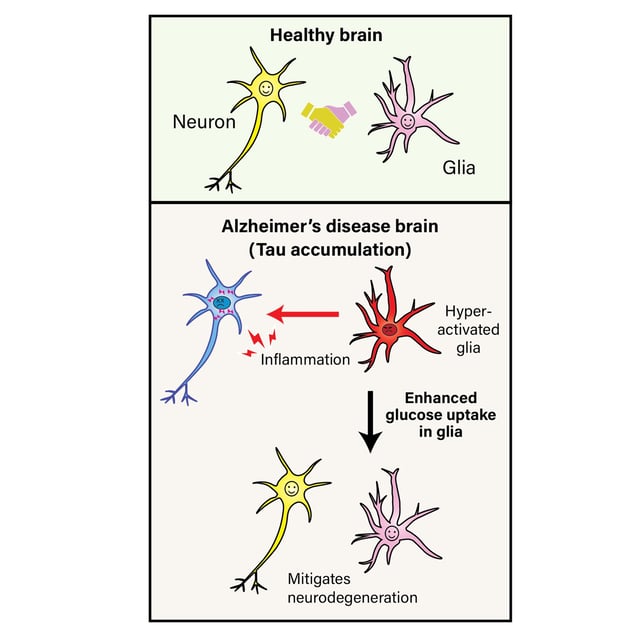
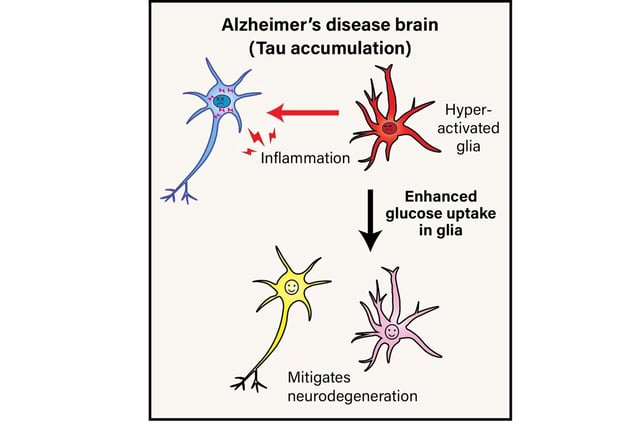
- Tokyo Metropolitan University researchers demonstrate that tau pathology disrupts glucose metabolism in glial cells, driving neuroinflammation and neuronal degeneration.
- Using a genetically modified Drosophila retina model, scientists observed that tau buildup caused a significant drop in glial glucose metabolism.
- Overexpression of the glucose transporter protein (GLUT) in glial cells suppressed inflammation and photoreceptor degeneration without altering tau levels.
- The findings position glial glucose metabolism as a promising therapeutic target for Alzheimer's and potentially other neurodegenerative diseases.
- Further preclinical studies are underway to validate these results and explore their applicability to mammalian and human systems.