Overview
- The study highlights that increasing dietary potassium, found in foods like bananas and broccoli, may reduce blood pressure more effectively than reducing sodium alone.
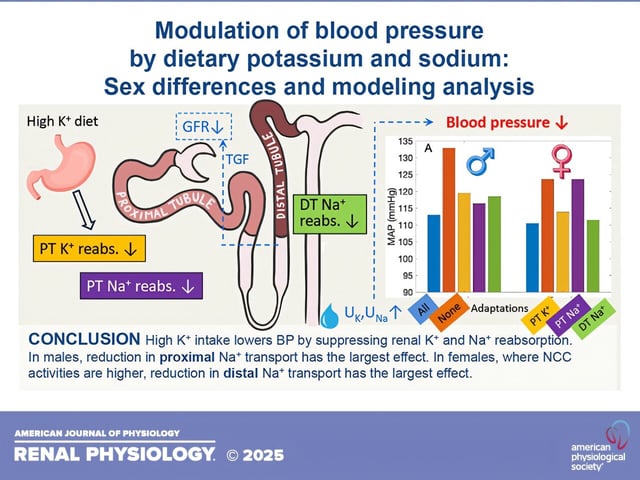
- A novel mathematical model developed by researchers quantifies the impact of the potassium-to-sodium ratio on blood pressure regulation.
- The research identifies sex-specific responses, showing men are more prone to high blood pressure but benefit more from an improved potassium-to-sodium ratio compared to premenopausal women.
- Findings suggest modern diets, high in sodium and low in potassium, contrast with evolutionary dietary patterns, potentially contributing to widespread hypertension in industrialized societies.
- Mathematical modeling offers a cost-effective and ethical method for studying dietary impacts on health, advancing public health strategies for managing chronic diseases like hypertension.